Infographic Blog
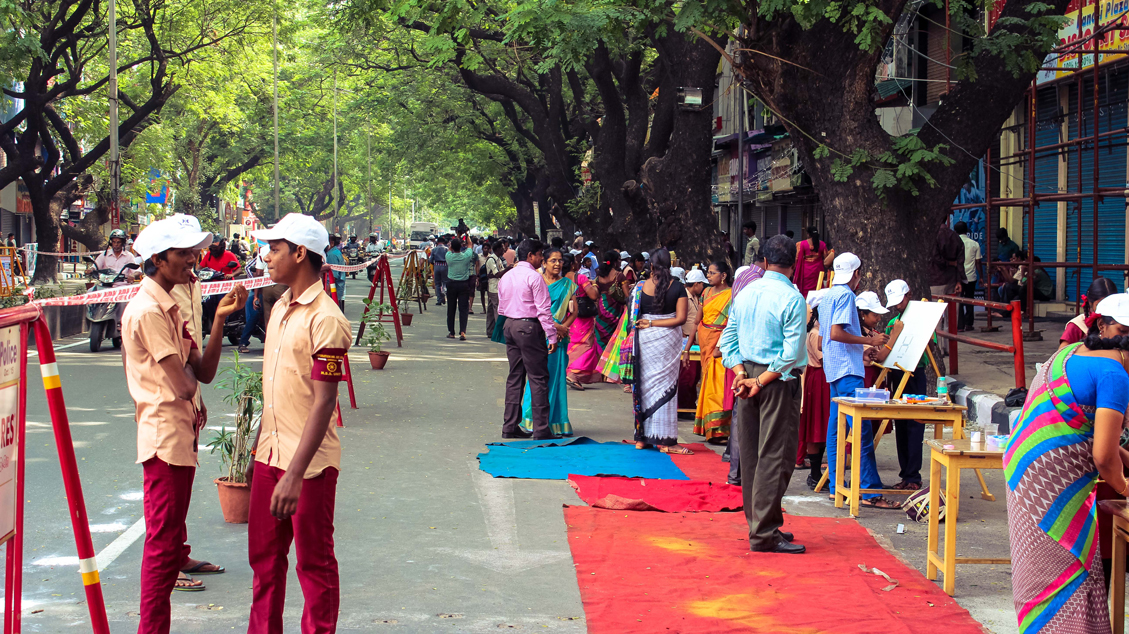
In an era of vanishing footpaths and widening carriageways, the Greater Chennai Corporation (GCC) has been introducing a host of initiatives prioritising pedestrians, cyclists and public transport users — giving these social heroes their due. From adopting a progressive policy that makes walking and cycling its priority in 2014, to rigorously implementing the policy through its Chennai Street Design Project and the Smart City Mission over the last five years, the city has been transforming itself from a car-centric to a people-friendly city.
Scaling up the street transformation work in Chennai, the Greater Chennai Corporation launched the Chennai Mega Streets Programme to create a city wide network of streets with a lifespan of at least 30 years – prioritising Liveability, Mobility and Utility. The success of the street transformation works and the Mega Streets launch was reflected in the Tamil Nadu Budget announcement in February 2020, with the allocation of funds for the preparation of DPRs and commencement of work.
With the Mega Streets Programme now set in motion, Chennai is now gearing up to become the “Walking Capital of the Country”. Learn more about the city’s journey of making Streets for People in the infographic below.

Conceptualized by: Aswathy Dilip, A V Venugopal, Santhosh Loganaathan









 NMT Masterplan
NMT Masterplan