Infographic Blog
“All urban residents of Indian cities should have access to jobs, education, and recreation through means of mobility that are safe, affordable, resource-efficient, environment-friendly, and accessible to all.”
Over the last 20 years, the ITDP India Programme has worked with nearly 40 cities across the country to make this vision a reality, impacting the lives of millions.
We celebrate the completion of a glorious decade of work, and welcome a new one with renewed excitement and anticipation of the possibilities ahead.

Designed by Keshav Suryanarayanan
Conceptualised by Aishwarya Soni, Keshav Suryanarayanan























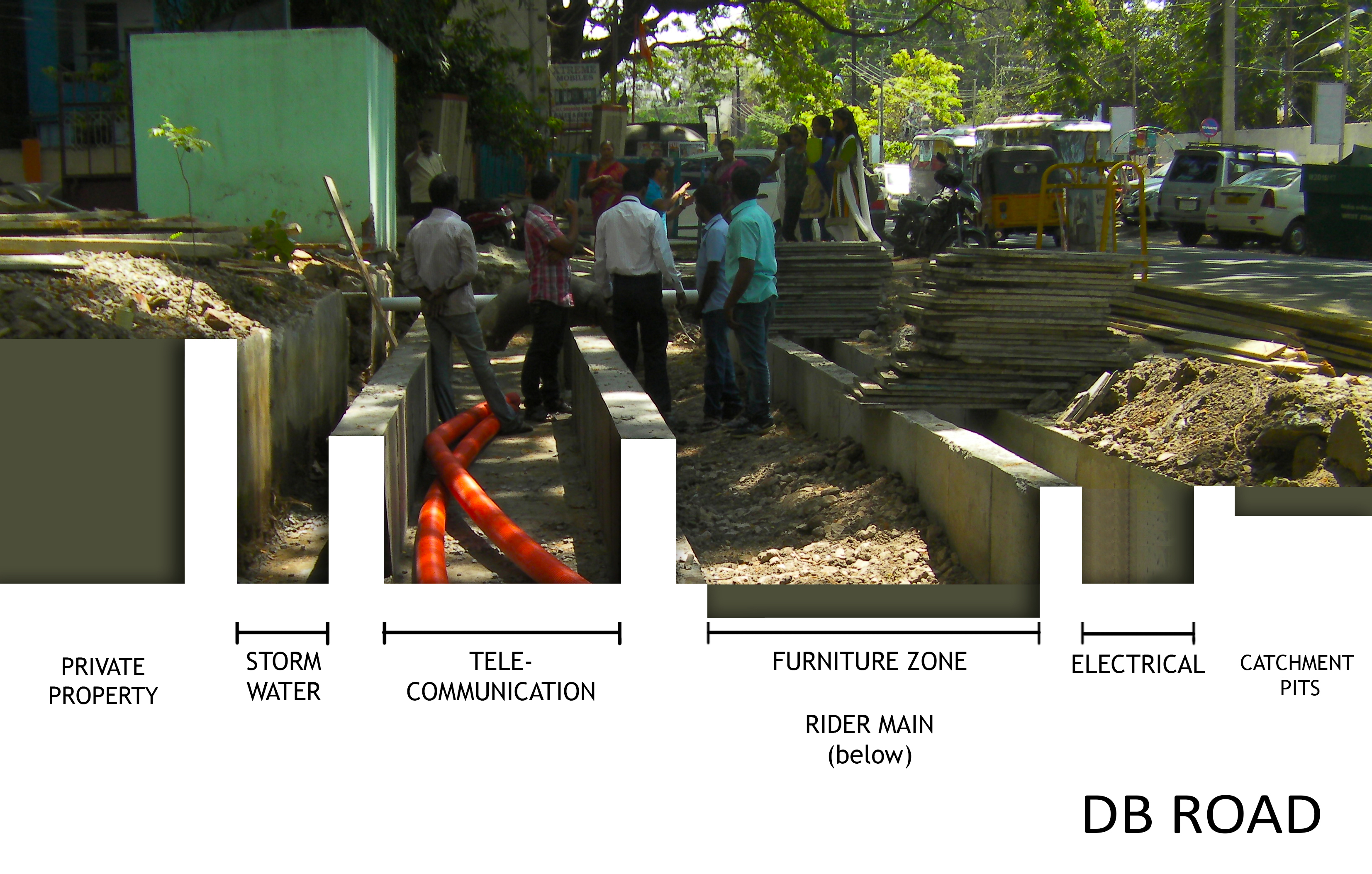
 Consultation with Nashik Municipal Corporation
Consultation with Nashik Municipal Corporation